Have you ever imagined what it would be like if you could save most of your production time? The winds of manufacturing are constantly changing. Additive manufacturing, which was first developed in the 1980s, was initially used just for prototyping, but today it has steadily surpassed traditional machining techniques that often took long periods to complete. However, there is still a lot of confusion and uncertainty about additive manufacturing, industrial parts manufactured using 3D Printers, the best 3D printer for end-use parts and many more. As we enter the age of mass customisation, 3D Printing would assist in eliminating the ‘stock outs’ and make products suitable for the customer’s exact requirements. In the 3D Printing process, the CAD file of the design is sent in for printing and within no time you have the desired part in your hands. Today 3D Printing has found its way into a wide array of industries like automotive, jewellery, research & development, healthcare, dental, aerospace, defence, education and more.
Additive Manufacturing allows design freedom for manufacturers. Right from flexible designs for complex shapes to having strong and lightweight jigs and fixtures to functional prototypes and even end-use customised parts, everything is possible under the 3D Printing umbrella. Manufacturers can choose from various materials, including different types of plastics, metals, composites, graphene and graphite. Additionally, various types of additive manufacturing technologies like Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), Digital Light Process (DLP), Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) and more can be chosen based on your application.
End-use Parts
An end-use part can be defined as a manufactured good that is ready to market or part of an assembly of products, or even a ready-to-use product in the company's internal operation. You as a manufacturer might be under constant pressure to get your products manufactured fast and with the highest quality. You want them ready to use or sell in the shortest time. Every once in a while, you might be considering and thinking if additive manufacturing is the solution for your problems and concerns and if it is right to leverage 3D Printing for manufacturing end-use parts too.
Many companies think 3D Printing suffices the need for prototyping, testing and refining but not the final product. In a typical manufacturing scenario, the prototypes are produced to test form, fit and functional capabilities and then the whole batch is either CNC machined or injection moulded. Today, however, many 3D-printed parts perform just as well (and in some cases even better) than conventionally produced parts. Additive manufacturing technology has evolved from an alien-like technology confined to labs to a technology loved by all. From figurines to gadgets to anatomies to large bumper parts and even toys, 3D Printing has come a long way. The opportunity for 3D Printing manufacturing for end-use parts are boundless and includes numerous materials from plastics, metals, biocompatible material and even food. Various manufacturing giants have started using 3D Printing technology for the manufacturing of their end-use parts.
A classic example of this is the use of 3D-printed fuel nozzles in an aircraft's LEAP engine, which saves the owners roughly around $3 million per plane annually. The LEAP engine, a commercial jet engine, was promised to burn less fuel than the existing engines and release fewer emissions. One of the many aspects to do this was through the tip of the fuel nozzle. The expert team from GE Additive came up with a concept of a walnut-sized object that housed 14 elaborate fluid passages. This design was elegant yet flawed as the tip of the interior geometry of the nozzle was too intricate. The fuel nozzle's specifications could only be met with 3D printing. This new tip was 25% lighter, 5 times more durable, and 30% more efficient than its predecessor.
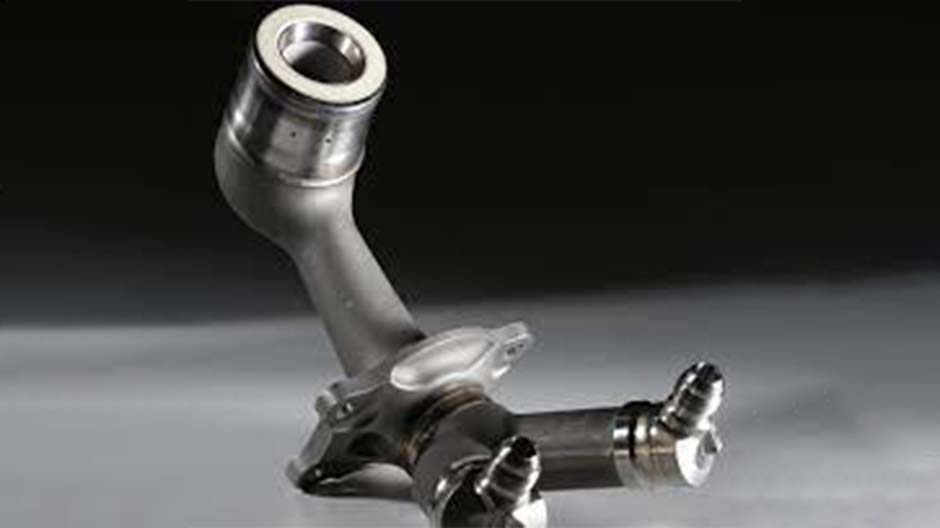

General Electric
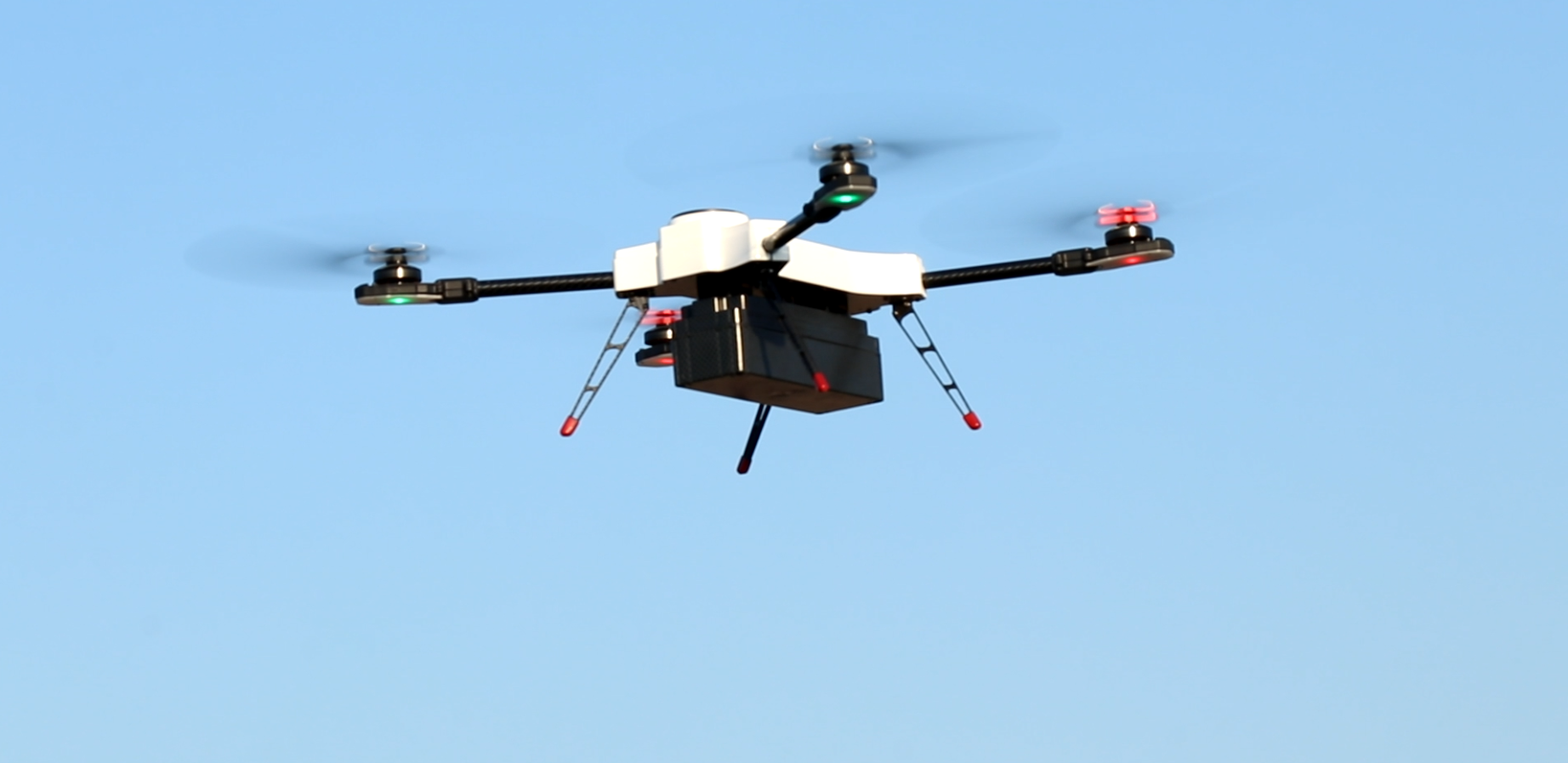
The world has a long-standing vision of flying cars. This has been possible only in the Harry Potter movies, but the use of drones has brought us a little closer to this dream. Drones are a new generation of mobility products that need extremely light parts, and this is possible with 3D Printing. When it comes to creating drones, almost every part of the assembly can be 3D printed like propellers, frames, antenna mounts, prop protectors, battery housing, circuit board and even the landing gear.

Benefits of Using 3D Printing for End-Use Parts
3D Printing is a technology that drives innovation and business growth. Some of the benefits of using 3D Printing for end-use parts include
1. On-Demand Production
3D Printing is revolutionising the production process. It enables manufacturers to produce physical parts from digital files in just a matter of hours. Therefore, companies can leverage a new model of manufacturing parts on-demand in a lesser time and cost-effectively. Imaginarium Smart Quoting and Manufacturing Platform assists manufacturers in producing end-use parts faster, better and cheaper. On-demand production assists in inventory reduction and bypasses the need for costly storage of parts that have low demand.
One such prime example of on-demand manufacturing is Siemens Mobility. They use 3D Printing to manufacture spare parts and tooling on-demand at the Siems Mobility RRX Rail Service Centre, with roughly 100 trains entering the depot each month. The 3D Printed parts reduce cost, reduce lead time from week to hours, and bring in greater operational agility.
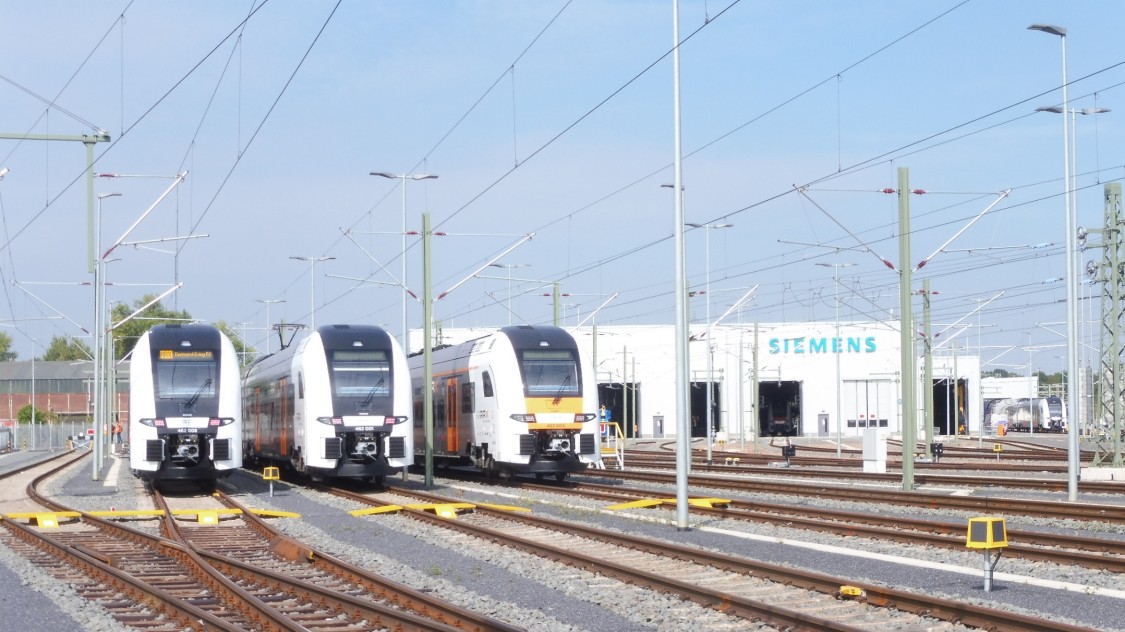

Siemens Mobility Solutions
2. Mass Customisation
One of the best benefits of using 3D Printing end-use parts is the potential of creating customised parts. In traditional manufacturing processes, products are made en masse. However, the manufacturing of customised parts in small batches can be highly inefficient and expensive if done with conventional methods.
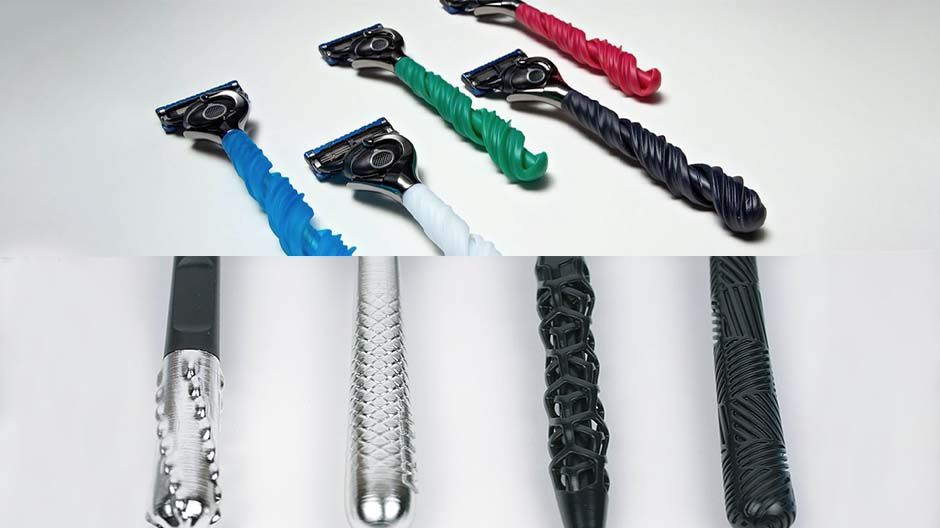
Gillette has also joined the bandwagon of customised mass 3D printing with custom razors. Gillette aims to give its customers razors that best suit their budget, look, colour and style. The Razor Maker platform from Gillette allows customers to choose from 48 design options to order customised shaver handles. There is no upfront investment in tooling as 3D Printing needs only a digital file and the printer to produce a batch of handles. Additionally, the design freedom that comes with this technology allows customers to enjoy entirely personalised razor handles.

3. Spare Part Management
When it comes to spare parts management, every manufacturer would want to balance the spare parts production cost, lead time and the volume of parts that must be stocked. When one opts for 3D Printing for end-use parts or spare parts, they find it economical and get a chance to opt for digital inventory. When there is a demand for a particular part, one can just see it in the digital inventory and send it to the 3D printer. The spare part will be ready within a short time.
Imaginarium revolutionised the making of legacy parts using a comprehensive design-to-manufacturing approach for their client in the oil and gas industry and provided the parts within just 15 days.
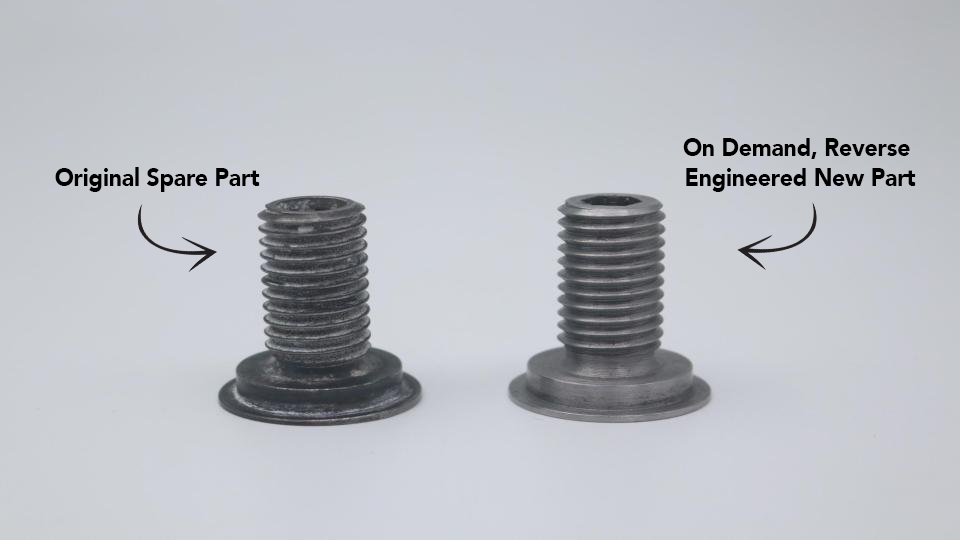
Imaginarium
4. Enhanced & Personalised Healthcare
Today medical device manufacturers have greater freedom in designing new products and creating patient-specific solutions that are not just time-saving but also cost-effective through additive manufacturing. In the medical field, precision, time and efficiency are everything. Every patient’s needs and body is different, as are every surgeon’s hands. Right from dental applications to prosthetics, fixtures, implants and more can be end-used directly on patients because of the use of biocompatible materials and the quick turnaround time. The first medical vertical to adopt 3D Printing technology was the dental field for their end-used parts.
Imaginarium was approached to create a cranial implant for a patient who lost a fragment of the skull. The traditional manufacturing method would result in higher costs, multiple iterations and numerous days, all of which were scarce and could lead to fatal results. Imaginarium collaborated with doctors to first create an accurate CAD model and then 3D printed a titanium implant that fit the patient's skull perfectly.
Additionally, the concept of one-size-fits-all surgical tools is outdated as one can 3D print them based on every individual's need. 3D Printed surgical instruments are not just a timely and affordable method, but they also improve the outcome and efficiency during surgery.
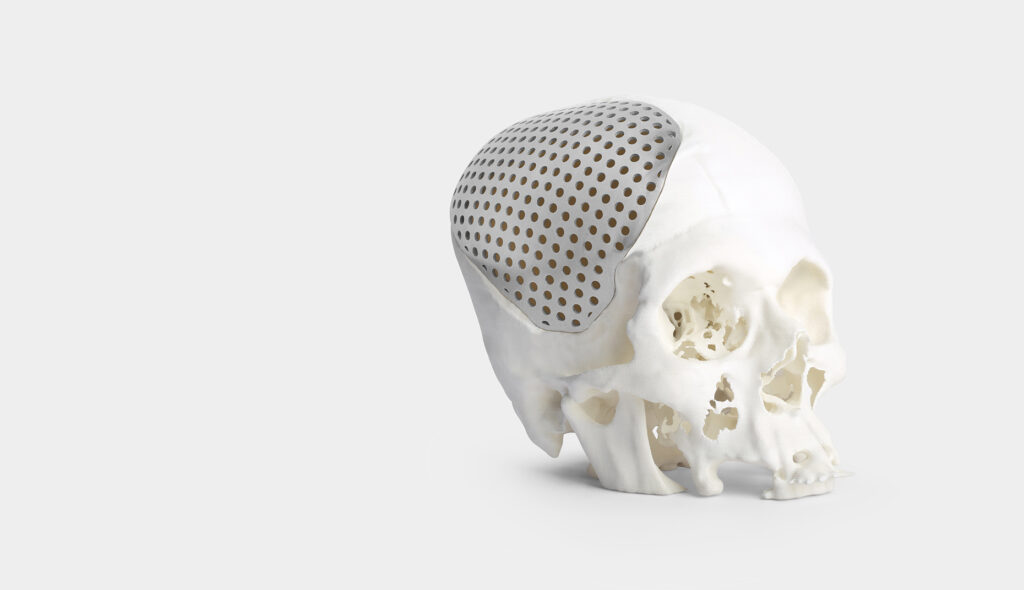
Imaginarium
5. Complex Design Flexibility
With 3D Printing, one can easily manufacture end-use parts that have complex designs effectively without any kind of extra machining cost including toys and high-end stationery. The designers have the flexibility to make quick design changes and modifications in a fraction of the time and at no additional cost. It’s not about the complexity only but also many 3D Printed parts have specific properties like heat resistance and higher strength.
Imaginarium manufactured a customised high-end 3D Printed metal pen that has high strength while maintaining low weight (27g) using medical-grade titanium with a lattice structure.
6. Weight Reduction
Many 3D Printing parts are lighter in weight compared to their counterparts. Light-weight parts are crucial for the automotive, drone and aerospace industries as they can deliver greater fuel efficiency. Our Design for Additive Manufacturing lets the manufacturers know design feasibility including wall thickness, the holes, traps, radii and reclamping, the weight and more. The experts would assist in reducing excess material and creating efficient design using topology optimization. Additionally, implicit design-based software is used to generate lighter designs using lattice structures that have high strength and lower mass.
General Motors (GM) created a 3D-printed version of an existing seat bracket whose design was based on specific parameters like weight, material, size and strength. The new 3D Printed seat bracket was 40% lighter and 20% stronger than the original and was manufactured as a one-component, unlike the original part which has to be assembled from 8 separate parts.
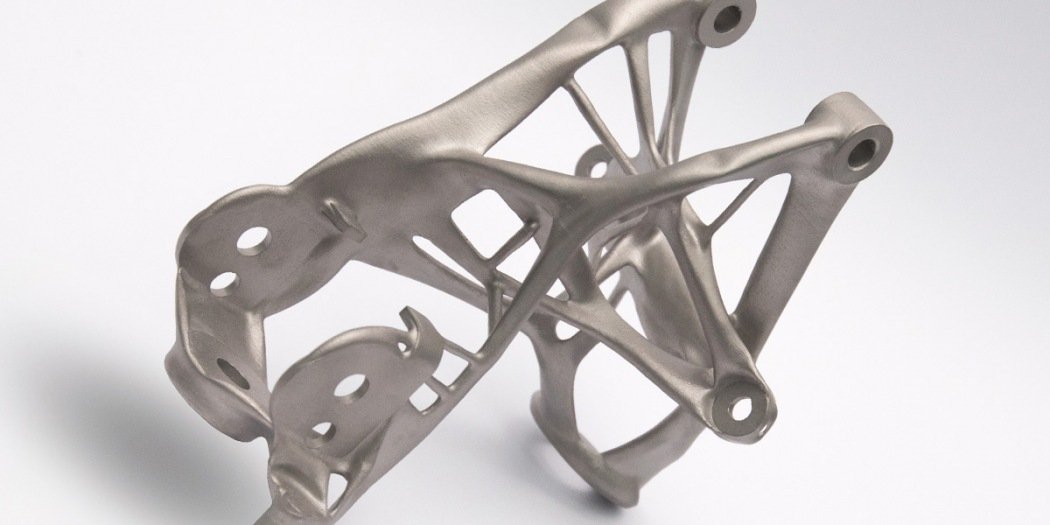

General Motors
The Future of 3D Printing for End-Use Parts
3D Printing is now moving beyond the boundaries of rapid prototyping. Many companies have already adopted this technology for serial production, and soon, many others would follow, making 3D Printed end-use parts a reality. Many industries think that this technology isn't mature enough to compete with the traditional manufacturing process, but this belief is being challenged continuously with every new case. Right from the dental industry to the space industry to automakers, everyone is moving towards 3D Printing technology. The true potential of 3D Printing as a manufacturing technology for end-use parts is now starting to unlock fully. Today, as many industries move towards smarter, digital technology, the relevance of 3D Printing for end-use parts is only going to increase.
Are you a manufacturer and tired of using cheap, plastic parts daily? Do you want to know how to get to the source of 3D Printed end-use parts? Would you like to incorporate this technology into your business? We are here to assist.
Just write to us at or give us a call on to speak to our 3D Printing expert.
